Crafting a Personal Financial Planning Spreadsheet: Step-by-Step Guide to Mastering Your Wealth
Financial planning is a challenge that everyone must face, especially in today’s world where rising prices and unpredictable financial markets are a daily concern. Many people have the desire to manage their finances wisely, but often lack a clear plan and actionable steps, which can make it difficult to achieve their financial goals. For the average person, a well-structured financial planning spreadsheet can not only help you clarify your objectives and allocate resources effectively, but also track your progress, preventing you from falling into the trap of impulsive spending or unwise investments. This article will guide you through the process of creating a detailed and practical financial planning spreadsheet, helping you better manage your finances in your day-to-day life.
1. The Basic Framework of a Financial Planning Spreadsheet
The core purpose of a financial planning spreadsheet is to help you clearly visualize all aspects of your financial situation, making it easier to analyze and adjust. A well-designed financial planning spreadsheet should include the following key sections:
- Assets and Liabilities Sheet: Lists all your assets and liabilities, helping you understand your current financial position.
- Income and Expense Sheet: Tracks all income sources and expense items, giving you an overview of your monthly cash flow.
- Budgeting Sheet: Helps you set monthly or annual budgets based on your income and expenses, preventing overspending.
- Investment Planning Sheet: Lists your current investments, sets investment goals, and assesses investment risks.
- Emergency Fund Sheet: Allocates a portion of your funds for unexpected emergencies, ensuring financial stability.
These sections form the basic structure of the financial planning spreadsheet. Each part helps you view your finances from different perspectives. By recording and analyzing this data, you can adjust your financial strategy and ensure you’re in control of your financial journey.
2. Constructing the Assets and Liabilities Sheet
Among the various sections in a financial planning spreadsheet, the assets and liabilities sheet is the most fundamental and essential. It allows you to immediately see your current financial situation. The sheet is typically divided into two categories: assets and liabilities.
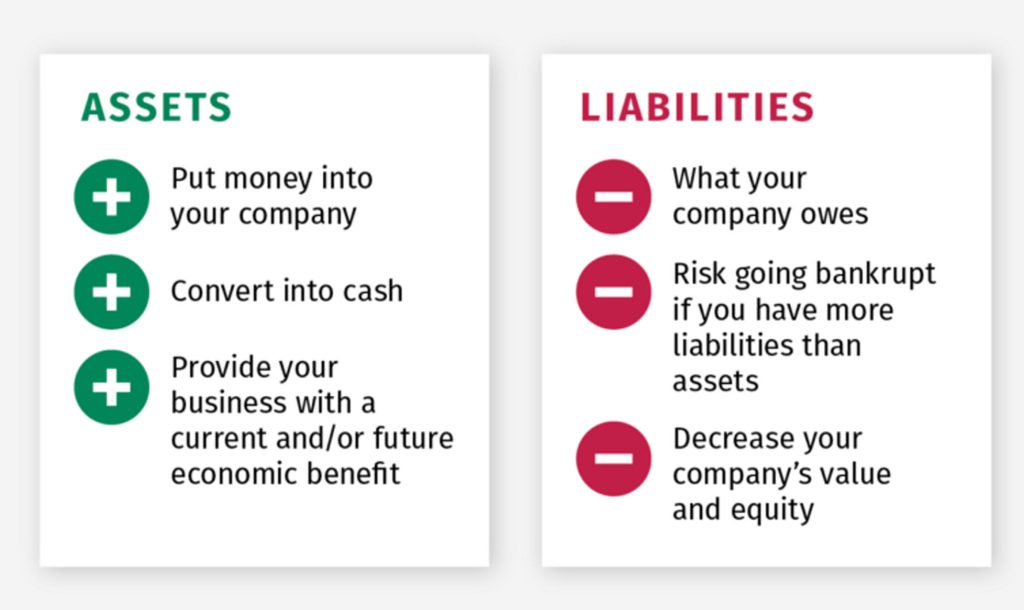
Assets Section
Assets are anything that holds financial value and can generate future economic benefits. Common assets include:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents: Bank deposits, cash on hand, short-term investments, etc.
- Real Estate: Property, land, and other tangible assets.
- Vehicles: Cars, motorcycles, and other vehicles with market value.
- Investments: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other financial assets.
- Pensions and Insurance: Retirement accounts and insurance policies designed for future savings.
Each asset should be listed with its specific value based on your current situation. For example, if you own a car, include its market value, the loan amount remaining on it, and its age. These details will help you accurately assess your net worth.
Liabilities Section
Liabilities refer to any debts that you are required to repay. These can include, but are not limited to:
- Mortgage: The amount owed on a home loan.
- Car Loan: Any outstanding balances on an auto loan.
- Credit Card Debt: Unpaid credit card bills.
- Personal Loans: Loans such as student loans or consumer loans.
Similarly, each liability should be listed with its amount, repayment term, and interest rate. This information is important for later adjustment and planning.
Through the assets and liabilities sheet, you can clearly determine whether your net worth is positive or if you’re in a situation with substantial debt. This sheet will help you make informed decisions about your financial future, such as whether to focus on reducing debt or increasing investment.
3. Income and Expense Sheet: Tracking Every Penny
The income and expense sheet is one of the most fundamental parts of financial planning. Only by understanding your income sources and expense categories can you effectively manage cash flow and allocate resources. The income section typically includes:
- Salary: The primary income for most individuals.
- Investment Income: Rent from real estate, dividends from stocks, etc.
- Side Income: Any additional income earned through freelance work or side jobs.
- Other Income: Gifts, bonuses, or unexpected windfalls.
The expense section is generally divided into fixed and variable expenses:
- Fixed Expenses: Regular, recurring payments such as mortgages, car loans, utilities, and insurance.
- Variable Expenses: Discretionary spending on groceries, entertainment, transportation, and shopping.
By tracking every income and expense item, you will have a clear picture of your cash flow each month. If you notice excessive spending or insufficient income, you can make adjustments based on the data from the spreadsheet—either by reducing unnecessary expenses or finding ways to increase your income.
4. Budgeting Sheet: Setting Realistic Financial Goals
The purpose of the budgeting sheet is to help you set financial goals and ensure that these goals are met within the specified time frame. With this sheet, you can break down large expenses into smaller, more manageable amounts, avoiding overspending.
For example, if you set a monthly living expense budget of $5000, covering items like dining, transportation, and entertainment, the budgeting sheet will help you monitor your actual spending each month. If you find that one category exceeds its budget, you can adjust other categories to maintain balance.
In addition to budgeting for everyday expenses, it’s equally important to have a budgeting plan for investments. You can allocate a specific amount each month or quarter for investments, ensuring you have the funds available for planned investment projects, and preventing your financial situation from becoming too tight due to excessive spending on investments.
5. Investment Planning Sheet: Growing Your Wealth
Investment planning is one of the most critical aspects of personal finance management. One of the primary reasons people fail in financial management is the lack of a solid investment plan. An investment planning sheet can help you clearly define the goals, risks, and returns of each investment, allowing you to make informed choices.
In the investment planning sheet, you can list your current investments, including:
- Stock Investments: Include the stocks you own, their purchase price, current market value, target returns, etc.
- Mutual Funds: List the funds you’ve invested in, including risk levels and expected returns.
- Real Estate Investments: For properties you own, record the purchase price, rental income, and potential for appreciation.
- Other Investments: This can include gold, bonds, private equity, or any other form of investment.
Each investment should be evaluated based on your risk tolerance, expected return, and liquidity. While planning investments, set clear objectives, such as aiming for a 10% return annually from stocks or earning rental income from real estate.
6. Emergency Fund Sheet: Preparing for the Unpredictable
An emergency fund is one of the most important and basic aspects of financial planning. No one can predict when an emergency will occur, whether it’s due to job loss, sudden illness, or an unexpected accident. Having an emergency fund can prevent you from falling into financial distress when these situations arise.
The general principle for setting up an emergency fund is to cover 3 to 6 months’ worth of living expenses. By consistently setting aside a portion of your income each month or quarter into an emergency fund account, you can ensure that you have financial security even if you lose your source of income. For the emergency fund, choose low-risk, high-liquidity investments, such as money market funds or fixed deposits.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Adjusting: Ensuring Financial Goals Are Met
A financial planning spreadsheet is not a one-time task—it requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Each month or quarter, you should review your asset-liability situation, income and expenses, and investment performance to ensure you’re on track.
For instance, if an investment is not yielding the expected returns, you may need to revise your strategy or switch to a different investment. If your spending exceeds the budget in one category, identify the cause and make adjustments to prevent the same situation from happening next month.
By regularly reviewing and adjusting your financial planning spreadsheet, you can continuously optimize your financial situation and stay on course to achieve your financial goals.
Financial planning is more than just a numbers game—it directly impacts your quality of life and financial security in the future. By meticulously designing and continuously refining your financial planning spreadsheet, you can steadily move toward your goal of financial freedom, ensuring that every dollar is maximized for long-term wealth growth.
