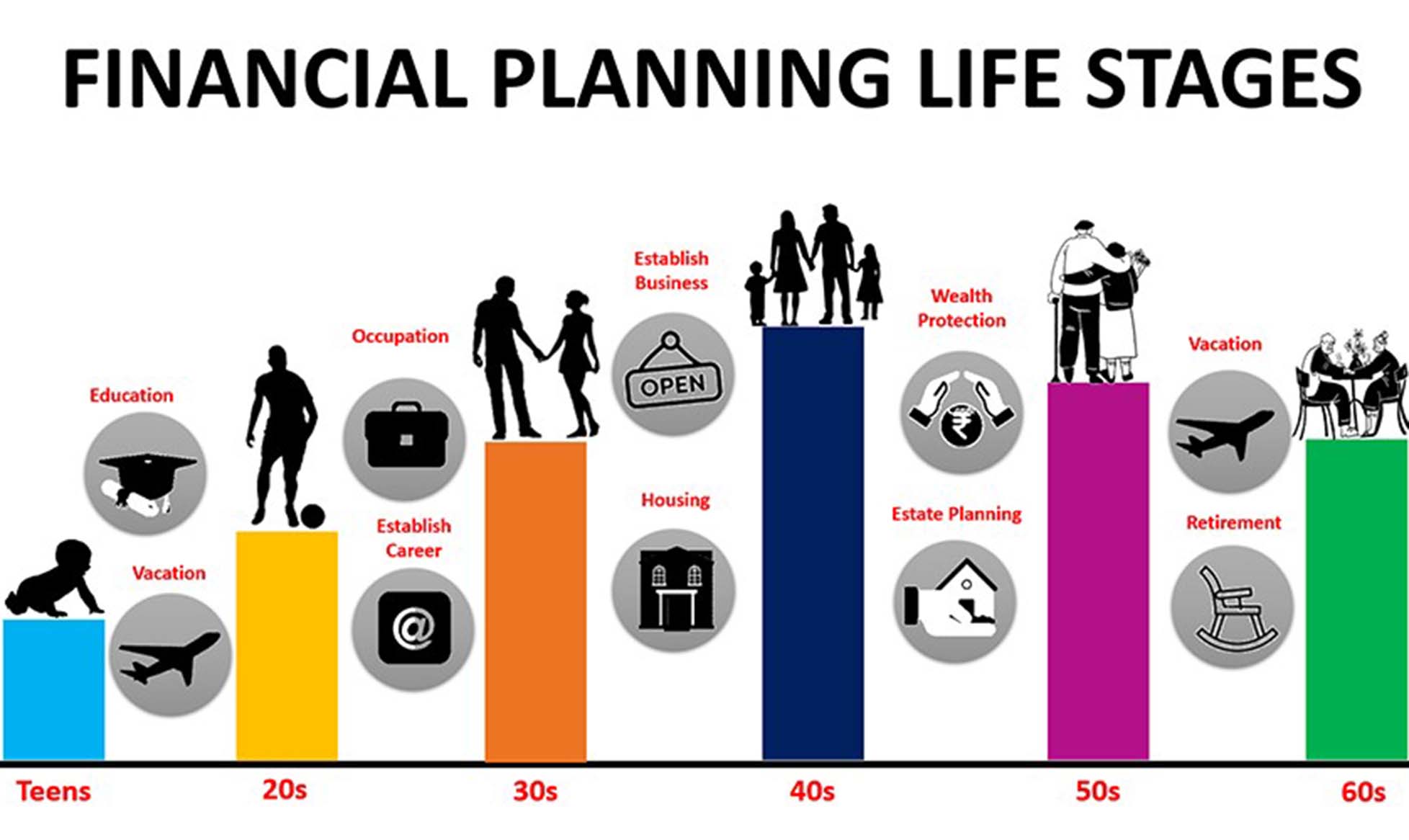
Financial Planning Through Different Life Stages: Every Step from Youth to Retirement
1. Youth Stage: Laying a Solid Foundation
Financial planning typically begins in the youth stage, usually after graduating from college or starting a career. At this stage, young people may not have much financial experience, but their decisions will lay the groundwork for their future financial situation. Therefore, early financial planning not only concerns income management but also includes managing investments, savings, debt, and the development of financial concepts.
1.1 Balancing Income and Expenses
When entering the workforce, many people face their first financial challenge: how to balance income and expenses. At the start of one’s career, the salary may be relatively low, so the key to financial management is learning to control expenses. Setting a detailed budget to ensure that monthly spending does not exceed income is the foundation. The first step is to distinguish between “necessary expenses” and “discretionary expenses.” For example, rent, food, transportation, and health insurance are necessities, while entertainment and shopping can be more easily controlled.
1.2 Learning to Save and Build an Emergency Fund
During the youth stage, one of the main goals of saving is to build an emergency fund. An emergency fund is intended to cover unforeseen events such as unexpected medical expenses, unemployment, or urgent repairs. It is usually recommended to set aside 3 to 6 months of living expenses in this fund. This ensures that, in the event of an emergency, there will be enough funds to maintain daily living without falling into financial hardship.
1.3 Student Loans and Debt Management
Many young people graduate with student loans, and managing this debt becomes a key aspect of financial planning. It is important to understand the interest rates and repayment terms for each loan and to create a clear repayment plan to avoid a debt crisis. Strategies such as the “debt snowball” method or the “debt avalanche” method can help manage loans. The debt snowball method involves paying off smaller debts first, gradually increasing the repayment amount, while the debt avalanche method prioritizes paying off high-interest debt to reduce the overall burden.
1.4 Starting Investment and Financial Management
Despite limited income, it is also important to start investing in the youth stage. Beginning with low-risk investment products, such as index funds or retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k) or IRA), is a good start. By regularly investing, even small amounts, the effect of compound interest will significantly accumulate over time. Youth is the golden period for compound growth—starting early means being able to leverage the power of time for wealth accumulation.
2. Family Stage: Wealth Growth and Protection
As one enters the family stage, financial planning becomes more complex. A family involves not only managing one’s own income and expenses but also the financial needs of a spouse, children, mortgage payments, education, healthcare, and more. The goal of financial planning at this stage typically focuses on wealth accumulation and providing sufficient economic support for family members.
2.1 Mortgage and Asset Management

Many families choose to buy a house, and a mortgage is often a significant financial burden. It is crucial to make an informed choice when selecting a mortgage product. Opting for a fixed-rate mortgage ensures that future monthly payments won’t be affected by interest rate fluctuations, making long-term financial planning easier. Additionally, when purchasing a home, one should consider the long-term appreciation potential of the property. Selecting a property in a favorable location and with good investment potential can ensure that the house contributes to future wealth growth.
2.2 Child Education Planning
After having children, education costs become a significant part of family financial planning. From kindergarten to college, educational expenses can consume a large portion of the family budget. Therefore, it is important to start saving for children’s education early, especially by utilizing tax-advantaged savings tools like 529 plans, which can help alleviate the future burden of high tuition costs.
2.3 Insurance and Healthcare Coverage
Financial planning during the family stage also requires special attention to health insurance and life insurance. Once children are born, ensuring that the entire family has adequate health insurance becomes a priority. In addition, purchasing appropriate life insurance is necessary to protect the financial stability of the family. If the primary breadwinner experiences an unexpected event, having the right insurance will provide the necessary economic support for the family.
2.4 Retirement Savings and Long-Term Investments
The family stage is a critical period for retirement planning. Although retirement may still be distant, starting to save and invest early will help accumulate sufficient retirement funds. 401(k), IRA, and other retirement accounts are key financial tools at this stage. By regularly contributing to retirement accounts, individuals not only enjoy tax advantages but also benefit from the compounding effect of investments to provide for a comfortable retirement.
3. Middle-Age Stage: Wealth Preservation and Growth
As people enter middle age, many have already established stable families and income sources. At this stage, the focus of financial planning shifts to wealth preservation and growth. The financial goals of this stage are no longer simply about survival but about achieving financial freedom, growing wealth, educating children, and accelerating retirement planning.
3.1 Investment Diversification and Risk Management
By middle age, the accumulated wealth is no longer small sums, but large savings and investments. At this stage, diversification of investments becomes especially important. To mitigate the risks associated with relying on a single investment, it is wise to allocate funds across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and mutual funds. Additionally, adjusting the investment portfolio according to one’s risk tolerance ensures that the risk level remains appropriate.
3.2 Real Estate Appreciation and Asset Allocation
Financial planning in middle age often involves optimizing asset allocation. Real estate has likely become an important part of the family’s wealth by this stage. Many people choose to buy larger homes or invest in real estate at this point. To achieve wealth growth, individuals can increase the value of their property through renting, reselling, or renovating. Properly managing and allocating these assets will help accelerate the growth of wealth.
3.3 Children’s Independence and Inheritance Planning
As children grow older, education expenses decrease, and the financial burden on parents gradually lessens. At this point, parents can focus more on their own wealth-building plans. Furthermore, middle age is an important period for inheritance planning. Establishing a trust or drafting a will ensures that assets will be smoothly transferred to the next generation, maintaining wealth continuity.
3.4 Accelerating Retirement Planning

One of the primary tasks in middle age is to accelerate retirement planning. As people age, the wealth accumulated becomes increasingly critical for future retirement needs. Therefore, greater attention should be given to the management of retirement accounts. It is a good idea to increase contributions to retirement funds, adjust investment strategies as needed, and plan for post-retirement living expenses to ensure that one’s standard of living remains high during retirement.
4. Retirement Stage: Conservative Wealth Management and Life Security
Upon reaching the retirement stage, the focus of financial planning shifts to conservative wealth management and securing a comfortable lifestyle. At this stage, the accumulated wealth is primarily used to support one’s quality of life after retirement. Therefore, taking a conservative approach to investments and managing funds prudently is essential.
4.1 Capital Safety and Preservation
After retirement, income typically no longer comes from employment but from pension funds, investment returns, and other sources. Therefore, ensuring the safety and steady growth of one’s funds becomes crucial. In this stage, it is advisable to focus on low-risk investment options such as bonds, blue-chip stocks, and other secure instruments. It is also important to maintain sufficient cash reserves to cover potential emergencies.
4.2 Pension Utilization and Tax Planning
In retirement, pension accounts become the primary source of income. Efficiently withdrawing from these accounts and planning for taxes becomes a key concern. When withdrawing pension funds, it is advisable to do so gradually to avoid a large tax burden. Understanding tax policies and arranging the inflow of funds in a tax-efficient manner can help maximize the utility of pension funds.
4.3 Lifestyle Adjustments and Budget Management
Retirement often leads to changes in lifestyle, as many retirees choose to reduce working hours or fully retire, focusing on hobbies and family life. During this time, financial planning is centered on maintaining a reasonable budget and adjusting spending according to actual needs. Even without a steady income, individuals can manage their expenses wisely to maintain their standard of living.
By following financial planning through different life stages, individuals can progressively achieve their financial goals, creating a clear and structured path for wealth accumulation and management.